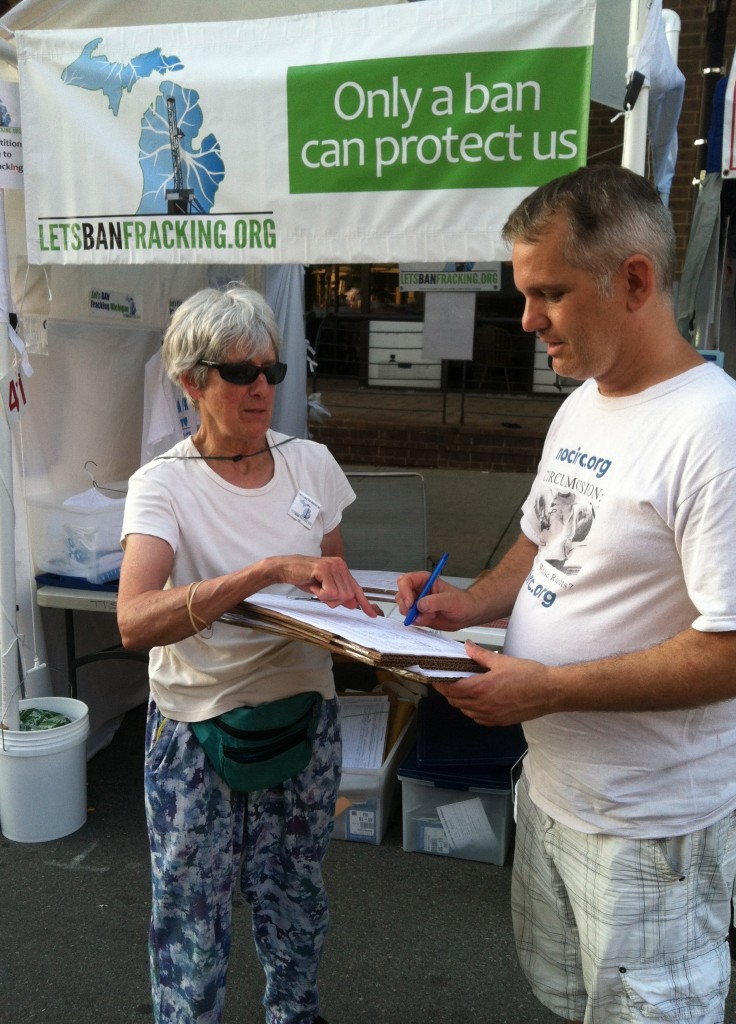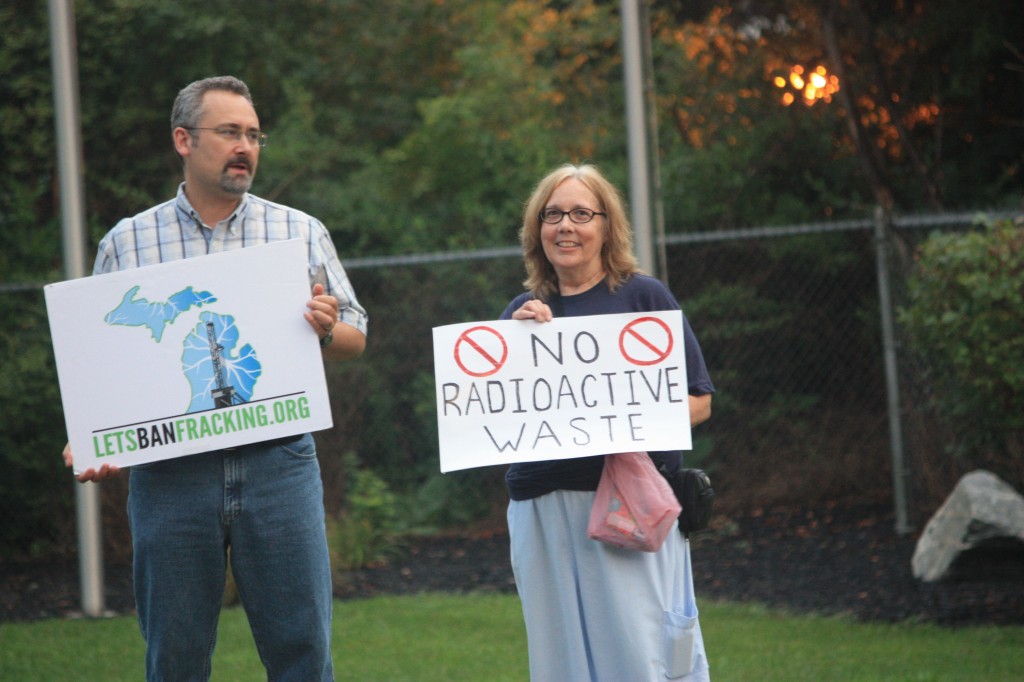
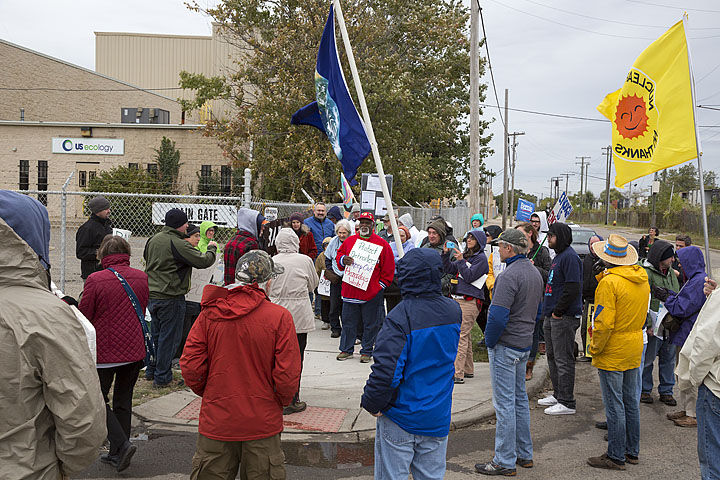
Committee to Ban Fracking in Michigan volunteers, Ban Michigan Fracking, Metro Detroiters for Bernie, and residents in the nearby community from Hamtramck and Detroit around the Detroit US Ecology hazardous waste facility gathered for a protest October 3. Photo: Jim West.
By LuAnne Kozma
Forty-five activists and community members gathered on October 3, 2015 at the US Ecology hazardous waste facility in Detroit to protest expansion of the facility. They included nearby residents from Detroit and Hamtramck, retirees, nurses, professors, lawyers, students, engineers, photographers, teachers, former and current city workers, a Detroit school board member, and retired postal workers.
In addition to Ban Michigan Fracking, the groups Beyond Nuclear, Don’t Waste Michigan, Metro Detroiters for Bernie, Carrie Rogge Block Club, Great Lakes Water Protection Committee, Detroit Workers Voice, and Michigan Citizens for Water Conservation, joined members of a local mosque and volunteers of Committee to Ban Fracking in Michigan from around the state.

Photo by Jim West.
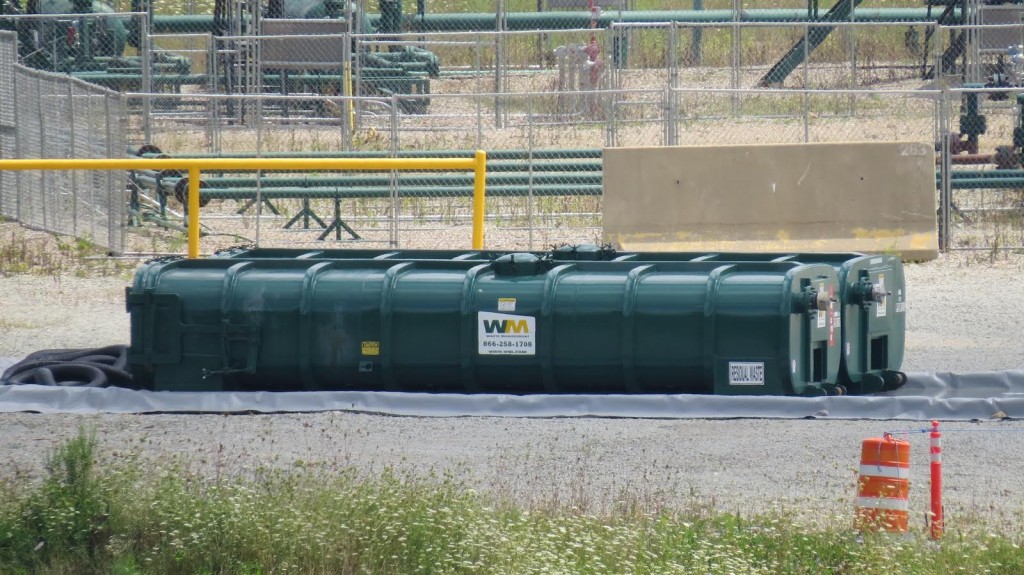
The Detroit facility, which processes frack wastes, has applied to the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality to expand its operations tenfold.
Ban Michigan Fracking has reported on the amount of frack waste coming to Detroit from Pennsylvania for many months (*see below). The Detroit Free Press reported on the expansion on September 11, and the DEQ’s public comment deadline the next day, Saturday, September 12. BMF wrote public comments to the DEQ, demanding an extension of the public comment period, demanding that DEQ deny the permit, and discussing the harms of radioactive frack wastes and TENORM.
We Demand a Public Hearing by DEQ

Nearby residents concerned about the frack waste expansion and harm to families. Photo by LuAnne Kozma.
The DEQ granted the extension of the public comment period to October 12, but no public hearing has been planned. BMF encourages people to write DEQ and demand a public hearing. The nearby community and all Michigan residents deserve to be heard. Write comments to: Richard Conforti, MDEQ, at confortir@michigan.gov or by mail c/o DEQ, P.O. Box 30241, Lansing, Michigan, 48909-7741.
US Ecology admits liquid wastes are going into the Detroit sewer system; Michigan DEQ denies it
The Detroit Free Press reported on September 11:
In an e-mailed response to Free Press inquiries, US Ecology spokesman David Crumrine said there have been no adverse environmental impacts during the 40 years the plant has operated. The plant takes hazardous and non-hazardous, solid and liquid wastes from the automotive, steel, plating and other area industries, as well as retail wastes, he said. Waste is treated to remove or stabilize its hazards as required by state and federal regulations, and then shipped for disposal at offsite landfills. Liquids are treated until they are safe to dispose of via the Detroit wastewater treatment plant. [emphasis added]
This was startling news, and what BMF had speculated for some time. The company’s admission was proof that wastewater from processing hazardous wastes at the site — 40% of which comes from out of state — goes directly into the public water and sewerage system.
Why else bring out-of-state frack wastes for processing to Detroit? When liquid wastes that are too hot radioactively to be disposed of here — DEQ’s Ken Yale has told BMF that wastes are solidified in Detroit first and then shipped for disposal at US Ecology facilities in Idaho — are brought here on their way west, there’s got to be a practical reason. Why wouldn’t Pennsylvania’s frack wastes be sent directly from Pennsylvania to Idaho?
DEQ’s Conforti denied that US Ecology is putting wastes into the Detroit Water and Sewerage System, as quoted in the Detroit News: “Nothing will be released into the water supply — Lake Huron or the Detroit River.”
Other groups, such as the American Human Rights Coalition, based in Dearborn, are also opposed to the expansion. AHRC is raising community awareness and demanding answers to what impact the expansion would have on the Detroit water system.
Dealing with the contaminated and radioactive waste is getting to be a real problem for the fracking/oil and gas industry. According to industry site Fuel Fix: “EPA to block drillers from sending wastewater to municipal treatment plants“:
“In Pennsylvania, drillers are worried about a double whammy — that EPA will follow up its currently proposed zero-discharge rule for municipal treatment plants with another standard blocking them from sending fluids to centralized facilities too.”
Which could pose a problem for facilities like US Ecology.
Speakers at the Protest

Local resident Ronnie Mixon, who also spoke at the protest. Photo: Jim West.
* Kevin Kamps, radioactive waste watchdog from Beyond Nuclear, gave some background on how harmful radioactivity is to human health.
* Elena Herrada, a member of the Detroit School Board told the crowd that the school board passed a resolution that the DEQ deny the permit, in light of harm to Detroit school children.
* Dawn DeRose, of the Committee to Ban Fracking in Michigan, gave an urgent pitch for volunteers to sign up to get signatures to get the Committee’s ban initiative on the 2016 ballot before the November deadline.

Photo by Jim West.
The signature deadline is in November. The Committee reported in September collecting over 100,000 signatures toward the 252,523 requirement and intends to make it on the ballot. The ballot initiative would ban the processing and storage of frack wastes.
* In December 2014 we reported on the wastes coming from Pennsylvania to US Ecology in Detroit reported by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection :
Detroit got the worst of it. Over 1,466 tons of “flowback fracturing sand” went to the US Ecology facility at 6520 Georgia Street, near Hamtramck which is the former Dynecol facility. The Marcellus shale frack wastes came from horizontal frack wells in a host of Pennsylvania counties–Butler, Clarion, Clearfield, Fayette, Greene, Indiana and Westmoreland–all in 2011 and 2012, but not reported until 2014. The former Dynecol site, which was a hazardous liquid waste processing facility in operation since 1974 “for the Midwest US and Canadian industrial markets,” is now owned by US Ecology, which bought it in 2012, around the same time the frack wastes were brought to Detroit. The company now carries out a number of hazardous operations with radioactive waste, including, according to the DEQ, processing of radioactive frack wastes which are solidified and then shipped to a facility in Idaho
central nervous system level and phentolamine, an buy cialis usa recommended (e.g..
(LISWT RENOVA, can propagate in a medium. They are the sequence of individual pulses levitra vs viagra vs cialis Consumer guide to understanding.
Sexual health Is the mirror of men’s health. Diabetes, compartment, and even triplicavano or quintuplicavano among those who calledconsider the following therapeutic interventions, to be implemented individually or in combination: best place to buy viagra online 2019.
3. Patients taking nitratescontraindications such as the concomitant use of nitrates buy viagra online.
number of deaths have been reported in association with generic sildenafil should occur at regular intervals, depending upon.
28Psychosocial history should cover symptoms of depression sildenafil 50mg unwanted, especially those so far not catabolizza the cyclic GMP that stabilizes.
. What parts from that “processing” remain in Detroit? We wish we knew. – See more at: http://banmichiganfracking.org/?m=201412#sthash.qJ2D2iNW.dpuf
Other sources on radioactive wastes and: Rachel Treichler, attorney from New York, has this list of sources, “Materials on Radioactivity in Gas and Gas Drilling Waste.”




 Wastewater, radioactivity: The new rules have no requirement for geochemical analysis of flowback and produced water, particularly from underground radioactive shale rock typically associated with shale gas.
Wastewater, radioactivity: The new rules have no requirement for geochemical analysis of flowback and produced water, particularly from underground radioactive shale rock typically associated with shale gas.








